Why the Indus Water Treaty Matters More Than Ever
The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) has stood as a beacon of international cooperation since its inception in 1960. Despite the political and territorial tensions between India and Pakistan, the treaty has allowed both nations to share the waters of the Indus River system peacefully. With global concerns about water security growing and environmental challenges intensifying, the Indus Water Treaty remains a crucial example of resource management and diplomacy in a contested region.

In this article, we’ll explore the Indus Water Treaty, its historical context, its evolution, the challenges it faces in 2025, and its future implications for both India and Pakistan. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or someone interested in international relations and water security, this detailed overview will help you understand why the treaty continues to play a vital role in South Asia’s geopolitics.
What Is the Indus Water Treaty?
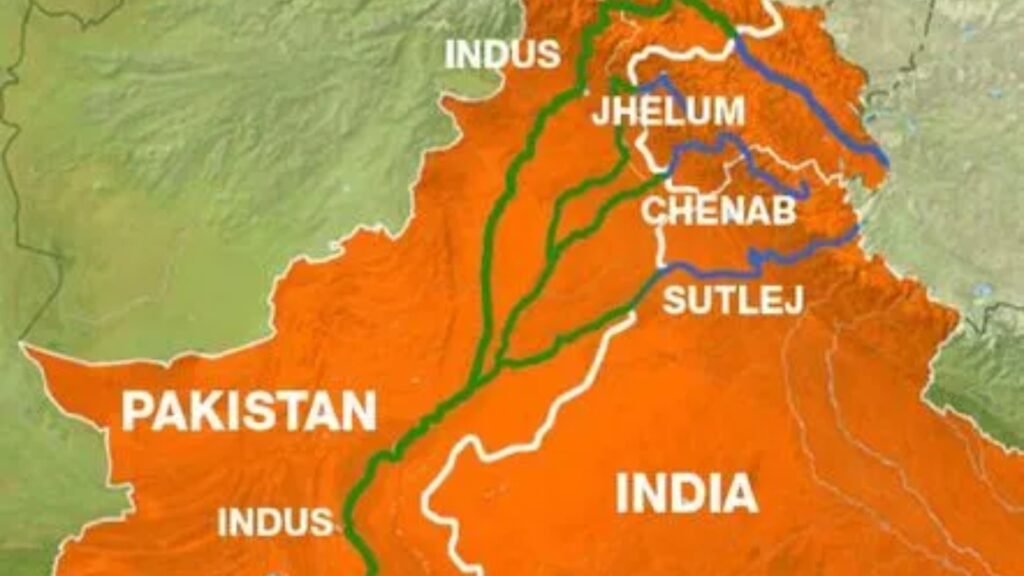
The Indus Water Treaty is an agreement between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank, that governs the allocation of water from the six rivers of the Indus River system: the Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej. The treaty allocates control of the rivers as follows:
- India controls the waters of the Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej).
- Pakistan has control over the Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab).
The treaty was signed in 1960 and has been widely regarded as one of the most successful international agreements on water-sharing, despite several tensions between the two nations.
Key Provisions of the Indus Water Treaty
Here are the most crucial aspects of the treaty:
- Water Allocation: The treaty divides the rivers into two categories—Eastern and Western—and allocates them to India and Pakistan accordingly.
- Usage Rights: India has the right to use the water from the Eastern Rivers for irrigation, power generation, and other purposes but cannot build any large-scale storage projects that could impede Pakistan’s access to the water.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism: The treaty includes a mechanism for resolving disputes. The Permanent Indus Commission, consisting of officials from both countries, plays a central role in ensuring compliance and addressing grievances.
- Development and Storage Projects: India is permitted to construct hydroelectric power projects on the Western Rivers, but these projects must be built in accordance with the specifications laid out in the treaty.
- Environmental Considerations: The treaty also highlights the environmental concerns related to water usage, including the need to ensure that both nations manage the rivers sustainably.
The Role of the Indus Water Treaty in South Asia’s Geopolitics
The Indus Water Treaty has not only served as a tool for resource-sharing but also as a diplomatic instrument in the volatile relations between India and Pakistan. Let’s break down how the treaty has influenced the geopolitical landscape:
1. Symbol of Cooperation Amid Conflict
Despite frequent political tensions and military conflicts, the IWT has managed to survive, standing as one of the few areas where India and Pakistan have cooperated consistently. Its continuation symbolizes a level of restraint and mutual understanding in a region known for volatility.
2. Economic Impact on Both Countries
Water is a critical resource in South Asia, especially for agriculture. The rivers covered under the treaty support millions of people, providing water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower. Any disruption in this flow could severely impact both countries’ agricultural sectors and economies. As such, the treaty plays a key role in preventing economic crises in the region.
3. Role of International Involvement
The World Bank played a pivotal role in facilitating the Indus Water Treaty, and its involvement is essential for the treaty’s continued success. The Indus Water Commission provides a platform for both countries to resolve water-related disputes, ensuring that the treaty remains functional and effective.
2025: Challenges and Controversies Facing the Indus Water Treaty
While the Indus Water Treaty has endured for over six decades, it faces several challenges in 2025. Let’s take a closer look at the key issues:
1. Climate Change and Water Scarcity
Climate change is making water availability increasingly unpredictable. Both India and Pakistan are facing water shortages, and the shrinking of glaciers in the region could further exacerbate water scarcity. In light of these challenges, the treaty’s ability to adapt to new environmental realities will be tested.
2. Infrastructure Developments by India
India’s plans for dam construction and hydropower projects on the Western Rivers have raised concerns in Pakistan. Despite the treaty’s provisions, there have been disputes over whether these projects comply with the agreement’s guidelines. The most notable project, the Kishanganga Hydroelectric Plant, has been a subject of contention.
3. Political Tensions
The Indus Water Treaty has been a source of political leverage during periods of tension between India and Pakistan. For instance, in 2016, following the Uri attack in Jammu and Kashmir, India threatened to revoke the treaty. Such threats raise questions about the long-term viability of the treaty in a politically charged environment.

Key Benefits of the Indus Water Treaty
Despite its challenges, the Indus Water Treaty offers significant benefits for both India and Pakistan:
- Water Security: The treaty ensures that both nations have access to critical water resources for agricultural and power needs.
- Peace and Stability: By fostering cooperation over a shared resource, the treaty helps maintain relative peace in a region marked by conflict.
- Conflict Prevention: By providing a clear framework for resolving disputes, the treaty minimizes the risk of water conflicts that could escalate into broader hostilities.
The Future of the Indus Water Treaty
As we move further into 2025, the future of the Indus Water Treaty will depend on:
- Collaborative Water Management: Both countries will need to address challenges like climate change, overuse, and environmental degradation together to ensure sustainable water management.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in water conservation and management technologies could help both nations utilize shared resources more effectively and equitably.
- International Mediation: The role of international agencies, such as the World Bank, in overseeing disputes and ensuring compliance will be crucial to the treaty’s longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What is the Indus Water Treaty?
The Indus Water Treaty is a 1960 agreement between India and Pakistan that governs the use of water from the Indus River system, ensuring fair distribution and preventing conflict over water resources.
Q2. Why is the Indus Water Treaty so important?
It is vital because it ensures that both India and Pakistan have access to critical water resources, helping prevent water-related conflicts in a politically volatile region.
Q3. How has climate change affected the Indus Water Treaty?
Climate change has resulted in unpredictable water flows, which could lead to shortages in the coming years, challenging the treaty’s current framework.
Q4. Can India alter the Indus Water Treaty?
While the treaty has provisions for dispute resolution, both nations would need to mutually agree on any modifications. India cannot unilaterally alter the terms.
Q5. How does the Indus Water Treaty affect Indo-Pak relations?
Despite tensions, the treaty has acted as a stabilizing factor, providing a structured mechanism to address water-related disputes and prevent them from escalating into broader conflicts.
Related Insights (People Also Search For)
- South Asia water disputes
- Climate change impact on South Asia rivers
- Pakistan water crisis
- India-Pakistan relations and water sharing
- Indus River basin geography
Conclusion: Preserving Peace Through the Indus Water Treaty
The Indus Water Treaty stands as a remarkable example of international cooperation. While challenges such as climate change and political tensions persist, the treaty’s ability to maintain peace and ensure fair water distribution makes it crucial for both India and Pakistan. As we move forward, adaptive management, technological innovation, and continued diplomacy will be essential to the treaty’s success.
Stay updated on the latest news and developments surrounding international treaties and regional cooperation. Explore more insights and stay informed with the latest updates at Chandigarh UT News & Events.









